This describes the command-line tools and API reference of the Axoflow Platform.
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Axoflow reference
- 1: AQL operator reference
- 2: Manual pages
- 2.1: axorouter-ctl
- 3: Message schema
- 3.1: Overview
- 3.2: Message schema reference
- 4: Metrics schema
- 5: Storage schema
1 - AQL operator reference
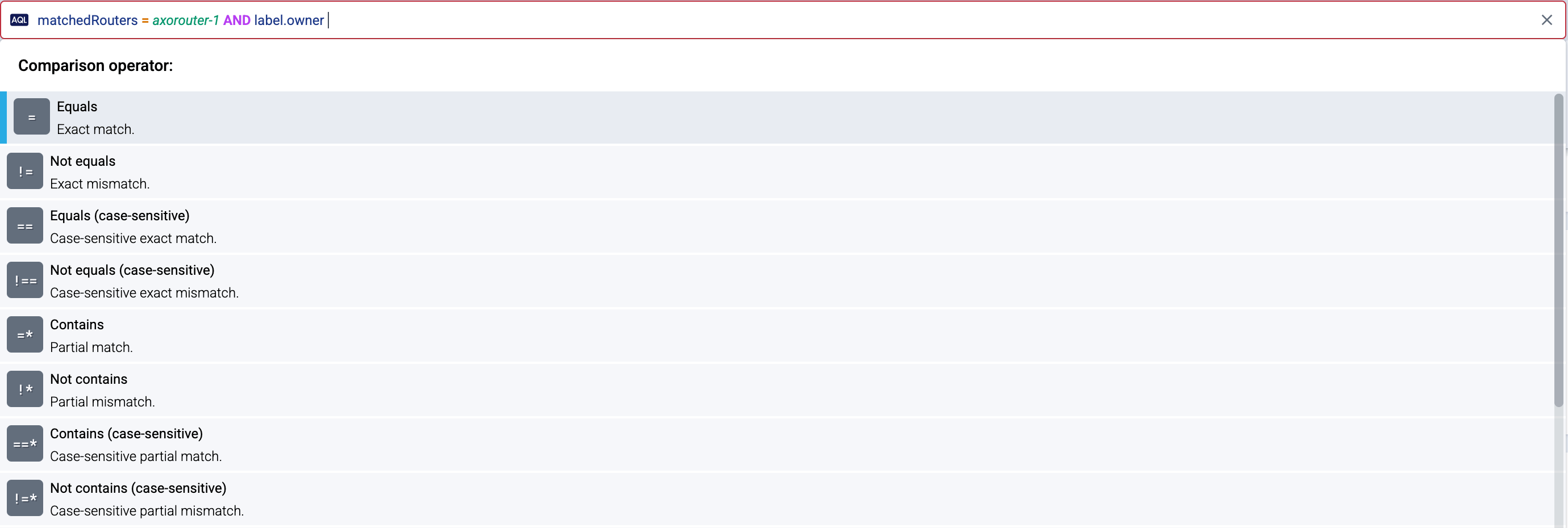
AQL Query search supports the following comparison operators.
Case insensitive:
- Equals (
=): the whole value equals to the pattern - Not equals (
!=): the value isn’t exactly equal to the whole pattern - Contains (
=*): the value contains the given pattern - Doesn’t contain (
!*): the value doesn’t contain the given pattern - Matches (
=~): the pattern as a regular expression matches the value - Doesn’t match (
!~): the case-insensitive regular expression doesn’t match
The comparison operators have their corresponding case sensitive (strict) versions:
- Equals (
==) - Not equals (
!==) - Contains (
==*) - Doesn’t contain (
!=*) - Matches: (
==~) - Doesn’t match (
!=~)
The syntax of the regular expressions accepted is the same general syntax used by Perl, Python, and other languages. The regular expressions are evaluated in case-insensitive mode in case of the =~ and !~ operators. The patterns are not anchored to the whole string, but you can use ^ at the beginning of the pattern and $ at its end to match the whole value.
You can create complex queries using the AND and OR logic operators and parentheses, for example, ( host_name =* azure AND host_label_team = network ) OR ( host_name =* app AND host_label_app =* windows )
Escaping rules
Enclose the field names and values in single-quotes ('), double-quotes ("), or \` if it contains characters not on this list: @, a-z, 0-9, ._-
If all three quote types occur, enclose with single-quotes and escape single-quotes as \\'.
You can escape backslashes as \\\\.
2 - Manual pages
2.1 - axorouter-ctl
Name
axorouter-ctl — Utility to control and troubleshoot AxoRouter
Synopsis
axorouter-ctl [command] [options]
Description
The axorouter-ctl application is a utility that is needed mainly for troubleshooting. For example, it can be used to:
- enable/disable troubleshooting messages
- display statistics about the processed messages
- display version information of AxoRouter.
Control syslog container
Usage: axorouter-ctl control syslog <command> <options>
This command allows you to access and control the syslog container of AxoRouter. Essentially, it’s a wrapper for the syslog-ng-ctl command of AxoSyslog. Usually, you don’t have to use this command unless our support team instructs you to.
For example:
- Enable debug messages for troubleshooting:
axorouter-ctl control syslog log-level verbose - Display the current configuration:
axorouter-ctl control syslog config --preprocessed - Reload the configuration:
axorouter-ctl control syslog reload
For details, see the AxoSyslog documentation.
Show logs
Usage: axorouter-ctl logs <target> <journalctl-options>
Displays the logs of the target container: syslog, store or wec. WEC logs are available only if the AxoRouter host has a ;Windows Event Collector (WEC) connector configured.
The axorouter-ctl logs command is a wrapper for the journalctl command, so you can add regular journalctl options to the command. For example, -n 50 to show the 50 most recent lines: axorouter-ctl logs syslog -n 50
Prune images
Usage: axorouter-ctl prune
Removes all unused images from the local store, similarly to podman-image-prune.
Pull images
Usage: axorouter-ctl pull
Download images needed for AxoRouter. This is usually not needed unless you have a custom environment, for example, proxy settings or pull credentials that aren’t available when the AxoRouter container is run.
Shell access to AxoRouter
Usage: axorouter-ctl shell wec
Open a shell into the target container (syslog, store or wec). Usually needed only for troubleshooting purposes, when requested by our support team.
Statistics and metrics
Usage: axorouter-ctl stats syslog <legacy|prometheus>
Display the statistics and metrics of the syslog container in Prometheus or legacy format, from the underlying AxoSyslog process. For details, see the AxoSyslog documentation.
Access AxoStore database
Usage: axorouter-ctl store
CAUTION:
Access the database directly only when instructed by the support team, or if you know exactly what you’re doing.Start an interactive SQL session using the command-line Clickhouse client to access data stored in AxoStore. Type exit to end the session.
Version
Usage: axorouter-ctl version
Show the version numbers of the underlying AxoSyslog build, for example:
0.58.0
axosyslog 4 (4.11.0)
Config version: 4.2
Installer-Version: 4.11.0
Wipe disk buffer files
Usage: axorouter-ctl wipe [-a/--all]
Deletes every corrupted and abandoned disk buffer files. Usually, you don’t have to use this command unless our support team instructs you to.
For disk buffer files containing messages, a backup copy is created into the /root/diskqueue_backup directory. To use a different directory for backups, set the BACKUP_DIR environment variable. This behavior can be overridden by the -a option, which deletes such files without making a backup. Empty disk buffer files are always deleted.
3 - Message schema
3.1 - Overview
When processing incoming data, AxoRouter automatically converts everything to its internal message model, and maps the contents of the model to the specific destinations as needed. The internal message model of AxoRouter is based on the OpenTelemetry Log Data Model, so what is sent to the destination is determined by the log section of the model (the main payload is log.body).
The meta section contains all the information and metadata AxoRouter has about the message: what was its source, how it was received, where it will be forwarded, how was it classified, and so on. You can use these metadata for example:
- in the processing steps of the flows,
- on the search interfaces of AxoConsole,
- during Flow tapping and Log tapping.
The related metrics of these data can be used:
- on the analytics pages, and
- in Flow tapping and log tapping filters.
When AxoRouter sends the message to its destination, parts of these metadata is automatically mapped into the relevant log field, but most of it (for example, labels) isn’t send to the destination by default.
For most destinations, there are specific fields that allow you to configure specific values that are sent to the destination, or to override the log.body field completely.
The message model has the following main elements:
3.2 - Message schema reference
Log (object)
The log data structure describes a log record.
log data structure describes a log record.
Log Attributes (object)
Additional attributes that describe the specific event occurrence. Every attribute key must be unique.
Log Body (string)
The body of the log record, which can contain strings and structured data composed of arrays and maps of other values.
Event date (observed) (number)
Time when the event was observed by the data pipeline, in UNIX Epoch time (nanoseconds elapsed since 00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970). A value of 0 indicates unknown or missing timestamp.
- For events that originate in OpenTelemetry, this timestamp is typically set at the generation time and is equal to
time_unix_nano.
- For events originating externally and collected by an Axoflow agent or an AxoRouter, this is the time when the Axoflow pipeline observed the event.
0 indicates unknown or missing timestamp.time_unix_nano.
Log Severity Number (number)
Numerical value of the severity, normalized to values described in Log Data Model.
Log Severity Text (string)
The severity as a string (log level). The original string representation as described at the source. For the numerical to string mapping, see log.severity_number.
Event date (number)
The time when the event occurred in UNIX Epoch time (nanoseconds elapsed since 00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970). A value of 0 indicates unknown or missing timestamp.
0 indicates unknown or missing timestamp.
Metadata (object)
Metadata about a specific message record, for example, a log message.
Classified (object)
The value of vendor, product, service name and other metadata set during classification.
Classified Product (string)
The product name of the source that generated the message, as determined by the classification.
Classified Service Metadata (object)
The name of the service that generated the message, as determined by the classification.
Classified Service Name (string)
Classified service Name for appliance.
Splunk metadata (object)
Splunk metadata extracted during classification.
Host (string)
The name of the host as sent to Splunk. Usually, this is the hostname of the source where the data originated from.
Splunk Index (string)
The name of the Splunk index where the message is sent. The index must exist in Splunk, otherwise sending the data will fail.
Splunk Source (string)
The source field sent to Splunk, containing where the event originated. For example, the protocol and port for network-based sources, or the path and filename for log files.
Splunk Sourcetype (string)
The Splunk sourcetype value that corresponds to the appliance, application, or service that generated the data.
Classified Vendor (string)
The name of the vendor of the source that generated the message, as determined by the classification.
Connection (object)
Information about the network connection that transmitted the message.
Destination IP address (string)
IP address where the message was sent to according to the IP header.
Related metric label: dest_ip
Destination port (number)
TCP or UDP port number where the message was sent to according to the transport header.
Related metric label: dest_port
IP protocol (number)
Network protocol version used for receiving this message.
Possible values: 4, 6
Related metric label: ip_protocol
Protocol (string)
Transport protocol used for receiving this message.
Possible values: TCP, UDP
Related metric label: protocol
Source IP address (string)
IP address that sent the message according to the IP header.
Related metric label: src_ip
Transport (string)
The transport mechanism used to retrieve or receive the message.
Example: rfc3164+tls
Related metric label: transport
Connector (object)
Information about the Connector that received the log. See the “attributes” column on the Connectors page for details.
Labels (object)
Labels set on the connector that received the message.
Prefix of related metric labels: connector_label_*
Name (string)
The name of the connector that received the log.
Example: myrouter-otlp
Related metric label: connector_name
Syslog Connector Related Metadata (object)
Parameters for processing the message from a Syslog source.
Splunk Log Type (string)
The type of the payload received from Splunk HF.
Possible values: syslog, plaintext
Type (string)
The type of the connector that received the message.
Possible values: otlp, soup, syslog, webhook, windowsEvents
Example: otlp
Related metric label: connector_type
Destination Connector (object)
Information about the Destination Connector.
AxoStore Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to an AxoStore destination.
Prefix of related metric labels: axostore_*
AxoStore Raw Body (boolean)
Override the option to send the raw message body to the AxoStore destination. (default: false)
AxoStore Raw Meta (boolean)
Override the option to send raw metadata to AxoStore destination. (default: true)
Azure Monitor Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to an Azure Monitor destination.
Azure Monitor Log Message (object)
Override the message sent to Azure Monitor. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Azure Monitor Stream Name (string)
Override the destination stream name in Azure Monitor. When set, stream-name configuration option is ignored.
stream-name configuration option is ignored.
Clickhouse Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to a Clickhouse destination.
Prefix of related metric labels: clickhouse_*
Clickhouse Raw Body (boolean)
Override the option to send raw body to the Clickhouse destination. (default: false)
Clickhouse Raw Meta (boolean)
Override the option to send raw metadata to the Clickhouse destination. (default: true)
Dynatrace Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to a Dynatrace destination.
Dynatrace Extra Fields (object)
Extra fields to add to the formatted Dynatrace Log Message.
Dynatrace Log Message (object)
Override the message sent to Dynatrace. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Elasticsearch Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to an Elasticsearch destination.
Prefix of related metric labels: elasticsearch_*
Elasticsearch Fields (object)
Fields to send to Elasticsearch. This overrides the default fields set by the destination connector.
Elasticsearch Index (string)
The Elasticsearch index to send the message to.
Elasticsearch Message (string)
Override the message to send to Elasticsearch. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Elasticsearch Timestamp (string)
Override the timestamp to send to Elasticsearch. When set, log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
Google SecOps Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to a Google SecOps destination.
Prefix of related metric labels: googlesecops_*
Google SecOps Customer ID (string)
This overrides the default customer ID configured in the destination connector.
Google SecOps Labels (object)
Labels to send to Google SecOps. This overrides the default labels set by the destination connector.
Google SecOps Log Text (string)
The text of the message to send to Google SecOps. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Google SecOps Log Type (string)
This overrides the default log type configured in the destination connector.
Google SecOps Namespace (string)
This overrides the default namespace configured in the destination connector.
Google SecOps Timestamp (string)
The timestamp of the message in RFC3339 format. When set, log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
Labels (object)
Labels set on the connector.
Name (string)
Name of the destination where AxoRouter sent the message.
Example: myrouter-splunk
Related metric label: destination_name
OpenObserve Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to an OpenObserve destination.
Prefix of related metric labels: openobserve_*
OpenObserve Fields (object)
Fields to send to OpenObserve. This overrides the default fields set by the destination connector.
OpenObserve Message (string)
Override the message to send to OpenObserve. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
OpenObserve Organization (string)
The OpenObserve organization to send the message to.
OpenObserve Stream (string)
The OpenObserve stream to send the message to.
OpenObserve Timestamp (string)
Override the timestamp to send to OpenObserve. When set, log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
Google Pub/Sub Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to a Google PubSub destination.
Prefix of related metric labels: pubsub_*
Google Pub/Sub Attributes (object)
Override the attributes key-value pairs for the Pub/Sub Event.
Google Pub/Sub Data (string)
Override the data to send to Google Pub/Sub. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Google Pub/Sub Project (string)
The ID of the Google Cloud project where the data is sent.
Google Pub/Sub Topic (string)
The name of the Google Pub/Sub topic to send the data to.
S3 Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to a S3 destination.
S3 Record (string)
Override the message sent to S3. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Security Lake Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to a Security Lake destination.
Security Lake Message (string)
Override the message sent to Security Lake. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Splunk metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to a Splunk destination.
Prefix of related metric labels: splunk_*
Event (string)
The raw event sent to Splunk. Overrides log.body and avoids automatic formatting completely.
log.body and avoids automatic formatting completely.
Splunk Fields (object)
Fields to send to Splunk. This overrides the default fields set by the destination connector.
Host (string)
The name of the host as sent to Splunk. Usually, this is the hostname of the source where the data originated from.
Splunk Index (string)
The name of the Splunk index where the message is sent. The index must exist in Splunk, otherwise sending the data will fail.
Splunk Source (string)
The source field sent to Splunk, containing where the event originated. For example, the protocol and port for network-based sources, or the path and filename for log files.
Splunk Sourcetype (string)
The Splunk sourcetype value that corresponds to appliance, application, or service that generated the data.
Splunk Time (string)
Override the time sent to Splunk. When set, log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
Sumo Logic Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to a Sumo Logic destination.
Sumo Logic Fields (object)
Fields to send to Sumo Logic. This overrides the default fields set by the destination connector.
Sumo Logic Message (string)
Override the message sent to Sumo Logic. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Sumo Logic Source Category (string)
Override the source category configured in the destination connector.
Sumo Logic Source Name (string)
Override the source name configured in the destination connector.
Syslog metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to a Syslog destination.
Syslog Message (string)
Override the message sent to Syslog. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Type (string)
Type of the destination, for example, splunkHEC.
splunkHEC.Possible values: azuremonitor, elasticsearch, openObserve, router, opentelemetry, pubsub, s3, splunkHEC, googleSecOps, sumologic, dynatrace, xsiam
Example: splunkHEC
Related metric label: destination_type
XSIAM Metadata (object)
Parameters for sending the message to an XSIAM destination
XSIAM Log Message (object)
Override the message sent to XSIAM. When set, log.body is ignored.
log.body is ignored.
Edge (object)
Information about the edge host and its resources that sent the message.
Connector metadata (object)
Metadata about the edge connector that sent the message.
Labels (object)
Labels set on the edge connector that sent the message.
Prefix of related metric labels: edge_connector_label_*
Name (string)
The name of the edge connector that sent the message.
Related metric label: edge_connector_name
Connector Rule ID (string)
The ID of the owner ConnectorRule resource in Axoflow that created the edge connector.
Related metric label: edge_connector_rule_id
Type (string)
The type of the edge connector that sent the message.
Possible values: windowsEventLog, windowsEventTracing, otelFile, otelJournald
Example: otelFile
Related metric label: edge_connector_type
Flow metadata (object)
Metadata about the edge forwarding rule that sent the message.
Name (string)
The name of the edge forwarding rule that sent the message.
Related metric label: edge_flow_name
Envelope (object)
Application metadata parsed from the envelope.
Envelope Extracted Service metadata (object)
Envelope Extracted service info about appliances.
Envelope Extracted Service Name (string)
Envelope Extracted Service Name for appliance.
Splunk metadata extracted from the message envelope (object)
Splunk metadata received from a Heavy Forwarder in the Axoflow envelope.
Host (string)
The name of the host as received from Splunk. Usually, this is the hostname of the source where the data originated from.
Splunk Index (string)
The name of the Splunk index where the message is received from.
Splunk Source (string)
The source field received from Splunk, containing where the event originated. For example, the protocol and port for network-based sources, or the path and filename for log files.
Splunk Sourcetype (string)
The Splunk sourcetype value that corresponds to appliance, application, or service that generated the data.
Message envelope type (string)
Type of the message envelope as detected by AxoRouter.
Flow name (string)
Name of the flow processing the message.
Related metric label: flow
Host (object)
Information about the host that sent the message.
Source Host Labels (object)
The labels set in the inventory for the host the message originates from. Note that if the host is sending data to an AxoRouter connector that doesn’t perform automatic classification, then changing the product and vendor labels can affect the final metadata in the destination, for example, the sourcetype assigned to the data in Splunk.
Prefix of related metric labels: host_label_*
Source Host Name (string)
The name of the host the message originates from (based on the inventory).
Related metric label: host_name
Host Candidate (object)
Device ID (string)
Device ID found in the message.
Related metric label: host_candidate_id
IP Address (string)
IP address found in the message.
Related metric label: host_candidate_ip
Host Name of the Last Hop (string)
Host field found in the message’s envelope (which can be either the subject of the message, or the name of the host that forwarded it).
Related metric label: host_candidate_last_hop_name
Host Name (string)
Host name found in the message.
Related metric label: host_candidate_name
Kubernetes (object)
Kubernetes metadata received from the collector.
Container Name (string)
Kubernetes container name found in the message metadata.
Related metric label: kubernetes_container
Namespace (string)
Name of the Kubernetes namespace found in the message metadata.
Related metric label: kubernetes_namespace
Product (string)
The product name of the appliance, application, or service that generated the message.
Related metric label: product
Router (object)
The name and labels of the AxoRouter instance that processed the message.
Labels (object)
Labels of the AxoRouter instance that processed the message.
Prefix of related metric labels: axo_host_label_*
Router Name (string)
The name of the AxoRouter instance that processed the message.
Related metric label: axo_host_name
Service metadata (object)
Information about the service that generated the message.
Service Name (string)
Name of the service that generated the message. For syslog messages, that’s usually the value of the PROGRAM field.
Related metric label: service
Vendor (string)
The vendor of the appliance, application, or service that generated the message.
Related metric label: vendor
Resource (object)
The resource data structure describes the resource that generated the log record.
resource data structure describes the resource that generated the log record.
Resource Attributes (object)
Attributes that describe the resource. Every attribute key must be unique.
Scope (object)
Log Scope representation
Scope Attributes (object)
Attributes that describe the log scope. Every attribute key must be unique.
Name (string)
Name of the log scope
Version (string)
Version of the log scope
4 - Metrics schema
The following list shows the metrics labels related to the message schema. You can use these metrics labels:
- on the analytics pages, and
- in log tapping filters.
dest_ip
IP address where the message was sent to according to the IP header.
dest_port
TCP or UDP port number where the message was sent to according to the transport header.
ip_protocol
Network protocol version used for receiving this message.
protocol
Transport protocol used for receiving this message.
src_ip
IP address that sent the message according to the IP header.
transport
The transport mechanism used to retrieve or receive the message.
connector_label_labels
Labels set on the connector that received the message.
connector_name
The name of the connector that received the log.
connector_type
The type of the connector that received the message.
axostore_axostore
Parameters for sending the message to an AxoStore destination.
axostore_body_raw
Override the option to send the raw message body to the AxoStore destination. (default: false)
axostore_meta_raw
Override the option to send raw metadata to AxoStore destination. (default: true)
clickhouse_clickhouse
Parameters for sending the message to a Clickhouse destination.
clickhouse_body_raw
Override the option to send raw body to the Clickhouse destination. (default: false)
clickhouse_meta_raw
Override the option to send raw metadata to the Clickhouse destination. (default: true)
elasticsearch_elasticsearch
Parameters for sending the message to an Elasticsearch destination.
elasticsearch_fields
Fields to send to Elasticsearch. This overrides the default fields set by the destination connector.
elasticsearch_index
The Elasticsearch index to send the message to.
elasticsearch_message
Override the message to send to Elasticsearch. When set, log.body is ignored.
elasticsearch_timestamp
Override the timestamp to send to Elasticsearch. When set, log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
googlesecops_google_secops
Parameters for sending the message to a Google SecOps destination.
googlesecops_customer_id
This overrides the default customer ID configured in the destination connector.
googlesecops_labels
Labels to send to Google SecOps. This overrides the default labels set by the destination connector.
googlesecops_log_text
The text of the message to send to Google SecOps. When set, log.body is ignored.
googlesecops_log_type
This overrides the default log type configured in the destination connector.
googlesecops_namespace
This overrides the default namespace configured in the destination connector.
googlesecops_ts_rfc3339
The timestamp of the message in RFC3339 format. When set, log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
destination_name
Name of the destination where AxoRouter sent the message.
openobserve_openobserve
Parameters for sending the message to an OpenObserve destination.
openobserve_fields
Fields to send to OpenObserve. This overrides the default fields set by the destination connector.
openobserve_message
Override the message to send to OpenObserve. When set, log.body is ignored.
openobserve_organization
The OpenObserve organization to send the message to.
openobserve_stream
The OpenObserve stream to send the message to.
openobserve_timestamp
Override the timestamp to send to OpenObserve. When set, log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
pubsub_pubsub
Parameters for sending the message to a Google PubSub destination.
pubsub_attributes
Override the attributes key-value pairs for the Pub/Sub Event.
pubsub_data
Override the data to send to Google Pub/Sub. When set, log.body is ignored.
pubsub_project
The ID of the Google Cloud project where the data is sent.
pubsub_topic
The name of the Google Pub/Sub topic to send the data to.
splunk_splunk
Parameters for sending the message to a Splunk destination.
splunk_event
The raw event sent to Splunk. Overrides log.body and avoids automatic formatting completely.
splunk_fields
Fields to send to Splunk. This overrides the default fields set by the destination connector.
splunk_host
The name of the host as sent to Splunk. Usually, this is the hostname of the source where the data originated from.
splunk_index
The name of the Splunk index where the message is sent. The index must exist in Splunk, otherwise sending the data will fail.
splunk_source
The source field sent to Splunk, containing where the event originated. For example, the protocol and port for network-based sources, or the path and filename for log files.
splunk_sourcetype
The Splunk sourcetype value that corresponds to appliance, application, or service that generated the data.
splunk_time
Override the time sent to Splunk. When set, log.time_unix_nano is ignored.
destination_type
Type of the destination, for example, splunkHEC.
edge_connector_label_labels
Labels set on the edge connector that sent the message.
edge_connector_name
The name of the edge connector that sent the message.
edge_connector_rule_id
The ID of the owner ConnectorRule resource in Axoflow that created the edge connector.
edge_connector_type
The type of the edge connector that sent the message.
edge_flow_name
The name of the edge forwarding rule that sent the message.
flow
Name of the flow processing the message.
host_label_labels
The labels set in the inventory for the host the message originates from. Note that if the host is sending data to an AxoRouter connector that doesn’t perform automatic classification, then changing the product and vendor labels can affect the final metadata in the destination, for example, the sourcetype assigned to the data in Splunk.
host_name
The name of the host the message originates from (based on the inventory).
host_candidate_id
Device ID found in the message.
host_candidate_ip
IP address found in the message.
host_candidate_last_hop_name
Host field found in the message’s envelope (which can be either the subject of the message, or the name of the host that forwarded it).
host_candidate_name
Host name found in the message.
kubernetes_container
Kubernetes container name found in the message metadata.
kubernetes_namespace
Name of the Kubernetes namespace found in the message metadata.
product
The product name of the appliance, application, or service that generated the message.
axo_host_label_labels
Labels of the AxoRouter instance that processed the message.
axo_host_name
The name of the AxoRouter instance that processed the message.
service
Name of the service that generated the message. For syslog messages, that’s usually the value of the PROGRAM field.
vendor
The vendor of the appliance, application, or service that generated the message.
5 - Storage schema
The following list shows the schema used when storing data in AxoStore. You can use these fields when searching on the Storage page.
log_attributes
Additional attributes that describe the specific event occurrence. Every attribute key must be unique.
body
The body of the log record, which can contain strings and structured data composed of arrays and maps of other values.
severity_number
Numerical value of the severity, normalized to values described in Log Data Model.
severity_text
The severity as a string (log level). The original string representation as described at the source. For the numerical to string mapping, see log.severity_number.
meta_raw
Metadata about a specific message record, for example, a log message.
connection
Information about the network connection that transmitted the message.
host_labels
The labels set in the inventory for the host the message originates from. Note that if the host is sending data to an AxoRouter connector that doesn’t perform automatic classification, then changing the product and vendor labels can affect the final metadata in the destination, for example, the sourcetype assigned to the data in Splunk.
host_name
The name of the host the message originates from (based on the inventory).
host_candidate
product
The product name of the appliance, application, or service that generated the message.
axo_host_labels
Labels of the AxoRouter instance that processed the message.
axo_host_name
The name of the AxoRouter instance that processed the message.
service
Name of the service that generated the message. For syslog messages, that’s usually the value of the PROGRAM field.
vendor
The vendor of the appliance, application, or service that generated the message.
resource_attributes
Attributes that describe the resource. Every attribute key must be unique.
scope_attributes
Attributes that describe the log scope. Every attribute key must be unique.
scope_name
Name of the log scope
scope_version
Version of the log scope